Orchids are captivating plants renowned for their unique and stunning flowers. To thrive, they require specific care tailored to their diverse needs. This guide will cover essential aspects of orchid care, including soil, light, water, and fertilization. Additionally, we’ll explore various types of orchids and their specific requirements, outdoor care, and other plant care tips.
1. Soil
Orchids are captivating plants renowned for their unique and stunning flowers. To thrive, they require specific care tailored to their diverse needs. This guide will cover essential aspects of orchid care, including soil, light, water, and fertilization. Additionally, we’ll explore various types of orchids and their specific requirements, outdoor care, and other plant care tips.
Orchid Mix – Most orchids thrive in a commercial orchid mix, which often includes bark, perlite, charcoal, and sphagnum moss. This mixture provides aeration and drains excess water efficiently.
Bark-Based Mixes -A mix of fir bark and sphagnum moss is ideal for orchids that need more moisture retention.
Perlite and Charcoal -These components improve drainage and prevent the growth of mold or fungi in the soil.
2. Light
Light is crucial for orchids to photosynthesize and bloom. Different types of orchids have varying light needs:
Phalaenopsis Orchids – Prefers bright, indirect light. Too much direct sunlight can scorch the leaves.
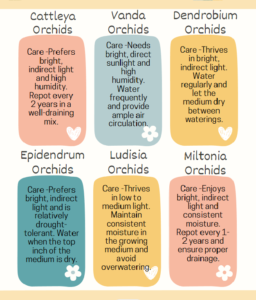
Cattleya Orchids – Requires bright, indirect light, possibly supplemented with morning sun.
Dendrobium Orchids – Thrives in bright, indirect light but can handle some direct sunlight.
Vanda Orchids – Needs bright, direct sunlight; in some cases, grow lights may be used indoors.
Ludisia Orchids – Prefers low to medium light conditions.
Ensure that your orchids are not placed in direct sunlight for prolonged periods, as this can lead to leaf burn.
3. Water
Orchids generally prefer a moderate watering regime. Overwatering is a common mistake, leading to root rot. Here’s how to manage watering:
Frequency-Water orchids about once a week, but this can vary depending on humidity, temperature, and pot size.
Method –Water thoroughly, allowing excess water to drain out. Ensure the potting medium is dry on top before watering again.
Water Quality-Use distilled or rainwater if possible, as tap water can contain minerals and chemicals that harm orchids.
4. Fertilizer
Proper fertilization supports healthy growth and flowering in orchids:
Type –Use a balanced, water-soluble fertilizer, such as 30-10-10 or 20-20-20.
Application –Feed orchids once a month during the growing season (spring and summer). Reduce feeding during the winter months when growth slows.
Dilution –Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for dilution to avoid over-fertilization, which can damage roots.
5. Orchid Care Outdoors
Orchids can be grown outdoors in appropriate climates. Here are some tips for outdoor orchid care:
Temperature – Most orchids require temperatures between 65°F and 75°F (18°C to 24°C). Protect them from extreme heat and cold.
Humidity – Orchids need high humidity. Consider using a humidifier or placing a shallow tray of water near the plants.
Protection – Ensure they are shielded from strong winds and intense midday sun. A shaded or filtered light environment works best.
6. Potted Orchids Care Outdoors
Potted orchids outdoors need special considerations:
Potting – Use pots with drainage holes to prevent waterlogging. Ensure the orchid mix is suitable for outdoor conditions.
Placement – Position pots where they receive filtered light or morning sun, and avoid direct afternoon sun.
Watering – Outdoor conditions can vary, so adjust watering frequency based on weather and humidity.
7. Planting Orchids in the Garden
Planting orchids directly in the garden is suitable for certain species and climates:
Location – Choose a location with dappled sunlight or filtered light. Avoid full sun and strong winds.
Soil – Amend garden soil with organic matter and improve drainage to mimic the orchid’s natural habitat.
Spacing – Space orchids adequately to allow for growth and air circulation.
8. Pesticides
Pesticides may be necessary to manage pests. Use them carefully:
Types – Neem oil and insecticidal soap are effective for many orchid pests, including aphids, spider mites, and scale insects.
Application –Follow the instructions on the pesticide label. Test a small area first to ensure it doesn’t harm the plant.
Alternatives – Regularly inspect plants and maintain cleanliness to reduce pest problems.
9. Repotting Orchids
Repotting is essential to refresh the growing medium and accommodate growth:
Frequency –Repot orchids every 1-2 years or when the medium breaks down. Spring is the best time for repotting.
Procedure – Gently remove the orchid from its pot, trim any dead roots, and place it in a new pot with fresh orchid mix.
Pot Size – Choose a pot slightly larger than the current one. Avoid oversized pots, which can lead to overwatering issues.
10. Choosing an Orchid
Selecting the right orchid involves considering your growing conditions and preferences:
Phalaenopsis – Ideal for beginners, these orchids are low-maintenance and bloom for several months.
Cattleya – Known for their fragrant and large blooms, suitable for intermediate growers.
Dendrobium – Offers a variety of flower types and colors, requiring moderate care.
Vanda – Requires bright light and high humidity, ideal for experienced growers.
Ludisia – Known for its ornamental foliage, best suited for low-light conditions.
11. Orchid Types and Care
12. More About Plant Care